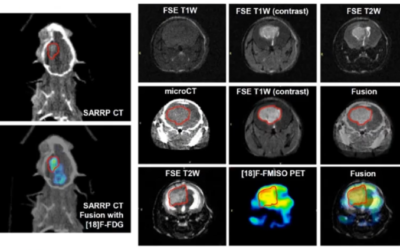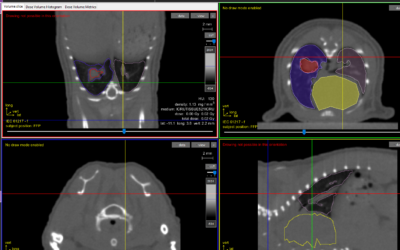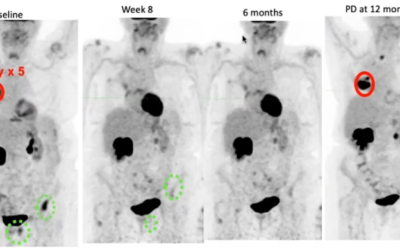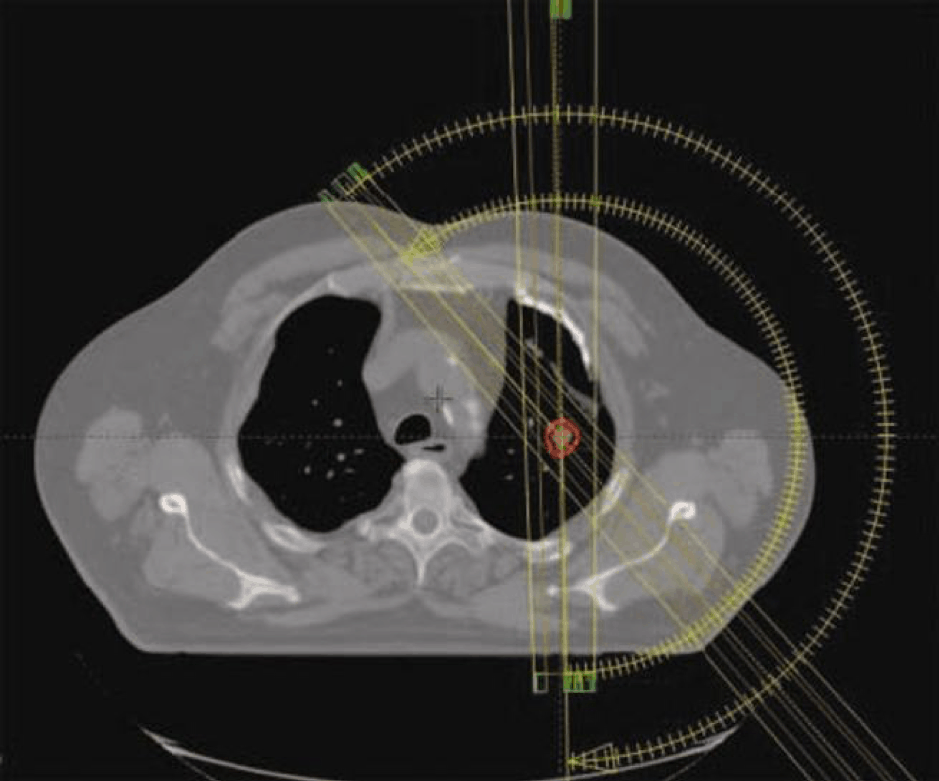
Stereotactic body radiation therapy offers good lung local tumor control by the administration of a high dose per fraction in small volumes. Stereotactic body radiation therapy preclinical modeling is now possible, and in their paper “Lung Stereotactic Arc Therapy in Mice: Development of Radiation Pneumopathy and Influence of HIF-1α Endothelial Deletion” Lavigne J, Suissa A, Verger N, Dos Santos M, Benadjaoud M, et al, aim to develop a model of focal irradiation of the mouse lung and to investigate the impact of conditional hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) deletion in the endothelium on radiation-induced tissue damage.
The Small Animal Radiation Research Platform was used to create a mouse model of focal irradiation of the lung using arc therapy. HIF-1α conditional deletion was obtained by crossing mice expressing Cre recombinase under the endothelial promoter VE-cadherin (VECad-Cre+/+ mice) with HIF-1α floxed mice.
Lung stereotactic arc therapy allows thoracic wall sparing and long-term studies. However, isodose curves showed that neighboring organs received significant doses of radiation, as revealed by ipsilateral lung acute red hepatization and major gene expression level modifications. Conditional HIF-1α deletion reduced acute lung edema and tended to diminish neutrophil infiltrate, but it had no impact on long-term global tissue damage.
Arc therapy for focal high-dose irradiation of mouse lung is an efficient model for long-term studies. However, irradiation may have a strong impact on the structure and function of neighboring organs, which must be considered. HIF-1α conditional deletion has no beneficial impact on lung damage in this irradiation schedule.
This Xstrahl In Action was adapted from an article found on a National Library of Medicine website.
SARRP Research Spotlight: Dr. George Wilson
George Wilson, PhD, Chief, Radiation Biology, William Beaumont Hospital Radiation Biology focuses on translational research in the areas of new treatments, combined modalities, and stem cell biology. The group has a heavy emphasis on incorporating molecular,...