Cancer treatment has come a long way in a short time, however as new drugs and treatments are developed, the therapeutic index of treatments needs to be assessed.
In their study “Inhibition of ataxia telangiectasia related-3 (ATR) improves therapeutic index in preclinical models of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) radiotherapy” Dunne V, Ghita M, et al, evaluate the impact of ATR inhibition using AZD6738 in combination with radiotherapy on the response of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tumour models and a murine model of radiation induced fibrosis.
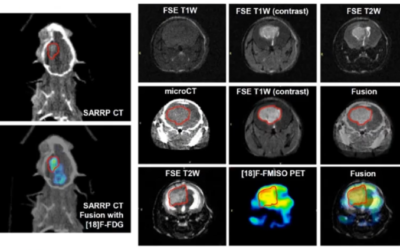
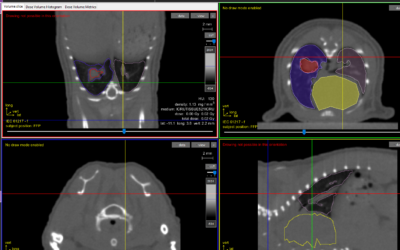
AZD6738 was evaluated as a monotherapy and in combination with radiation in vitro and in vivo using A549 and H460 NSCLC models. Radiation induced pulmonary fibrosis was evaluated by cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) and histological staining using the Xstrahl SARRP.
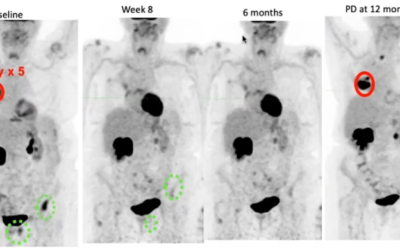
AZD6738 specifically inhibits ATR kinase and enhanced radiobiological response in NSCLC models but not in human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs) in vitro. Significant tumour growth delay was observed in cell line derived xenografts (CDXs) of H460 cells (p<0.05) which were less significant in A549 cells. Combination of AZD6738 with radiotherapy showed no significant change in lung tissue density by CBCT (p>0.5) and histological scoring of radiation induced fibrosis (p>0.5).
It was concluded that the inhibition of ATR with AZD6738 in combination with radiotherapy increases tumour growth delay without observable augmentation of late radiation induced toxicity further underpinning translation towards clinical evaluation in NSCLC.
This Xstrahl In Action was adapted from a article found on a National Library of Medicine website.