Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide and the fastest growing malignancy in the United States. With a 5-year survival rate below 12%, effective therapies for HCC are needed. Current treatments for HCC include microwave and radiofrequency ablation, high intensity focused ultrasound, liver transplant, surgical resection, and localized embolizations.
Each of these approaches has some limitation, making it imperative to develop improved methods for sensitizing tumors prior to therapy. In their paper “Localized microbubble cavitation-based antivascular therapy for improving HCC treatment response to radiotherapy.” Daecher A, Stanczak M, Liu JB, Zhang J, Du S, Forsberg F, Leeper DB, Eisenbrey JR hypothesized that the use of ultrasound-triggered microbubble destruction (UTMD), which sensitizes tumors to radiotherapy by inducing vascular endothelial cell apoptosis, will selectively sensitize malignant tissue to radiotherapy and improve outcomes.
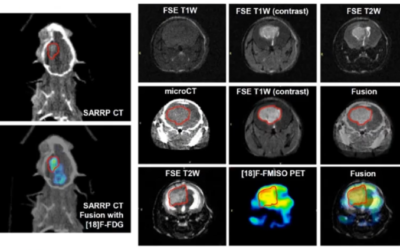
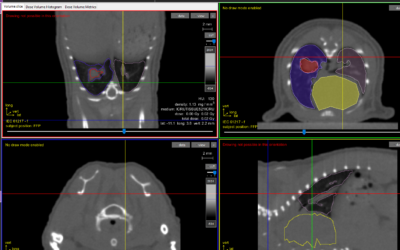
To test this, 18 nude rats were inoculated in the right liver lobe with Hu7.5 HCC cells and after tumor formation, received 5 Gy radiotherapy using the Xstrahl Small Animal Radiation Research Platform, UTMD, or UTMD prior to radiotherapy.
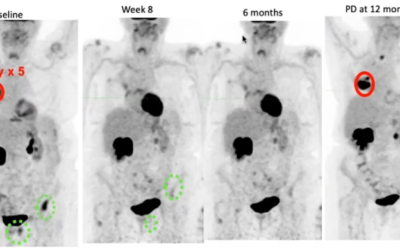
They found that compared to radiotherapy alone, there was a 170% reduction in tumor growth 7 days post treatment and a 3.2X improvement in median survival time when radiotherapy was combined with UTMD. These results indicate that UTMD is an effective adjunct when combined with radiotherapy to treat HCC.
This Xstrahl In Action was adapted from a article found on a National Library of Medicine website.