Review of Kalabasi A, Komar CA, Tooker GM, Liu M, Lee JW, Gladney WL, Ben-Josef E, Beatty, GL. Tumor-derived CCL2 mediates resistance to radiotherapy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clinical Cancer Research. 2016
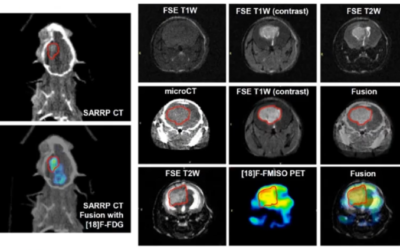
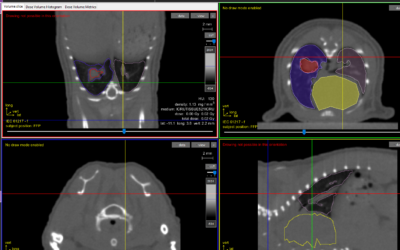
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is characteristically radioresistant tumor type with roughly 25% of patients requiring radiotherapy as form of treatment. With poor clinical outcomes (5-year survival of 7%) new and innovative treatments are required to improve patient outcome. Due to the lack of an effective treatment in the clinic for PDAC, translational research yielding clinically relevant results is necessary to develop new and effective treatment. SARRP technology allows for researchers in the pre-clinic to mimic clinical dose planning, delivery, and modeling which translates to more accurate, clinically relevant data.
The ability to combine radiation therapy with immunological based drugs is a new and exciting area of research. A recent study out of Abramson Cancer Center at the University of Pennsylvania has investigated combining immunotherapy (anti-CCL2 antibodies) and radiation (14-20Gy single fraction) to more effectively treat pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
Using the SARRP, Kalabasi et al. was able to mimic stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy (SBRT or SABR) in both ectopic and orthotopic tumor models of PDAC. Here, the researchers claim that ablative RT alone induces expression of CCL2 within the tumor microenvirionment which recruits inflammatory monocytes and macrophages which ultimately promote resistance to radiotherapy. When combining RT and antibodies against CCL2, a significant decrease in inflammatory monocyte recruitment was observed which corresponded with decreased tumor cell proliferation, vascularity, local disease control, and improved survival. Together these data suggest a new and novel way of combining RT with immunotherapy to improve outcome in patients with PDAC.
Link to article: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27354473
This Xstrahl In Action was adapted from a article found on a National Library of Medicine website.